Not satisfied with the unit price? Get a free quote on bulk quantities within 8 hours.
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
The Ultimate Guide to the Trendelenburg Position
The Trendelenburg position is a tilted supine position used by surgeons to facilitate access to surgical sites. It is typically used in lower abdominal surgeries. In recent times, various medical equipment like the operating table and hospital beds now incorporate this position into their designs.
Here we'll discuss the Trendelenburg position, its use, possible risks, and other hospital equipment that incorporates this position. Read on!
What is the Trendelenburg position?
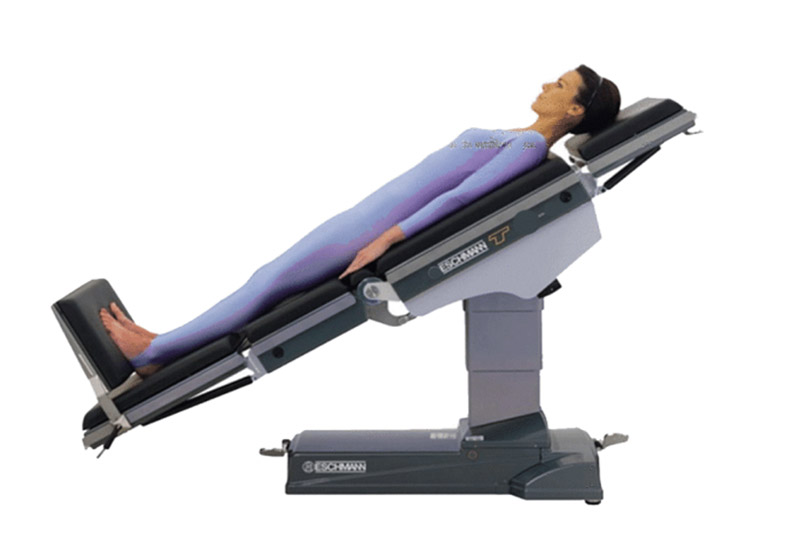
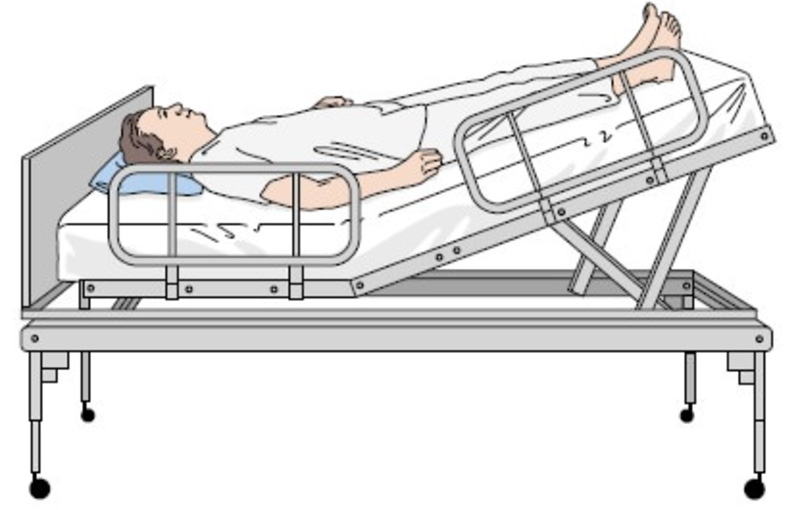
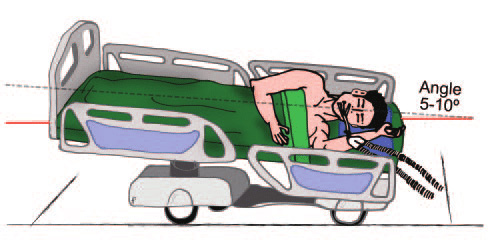
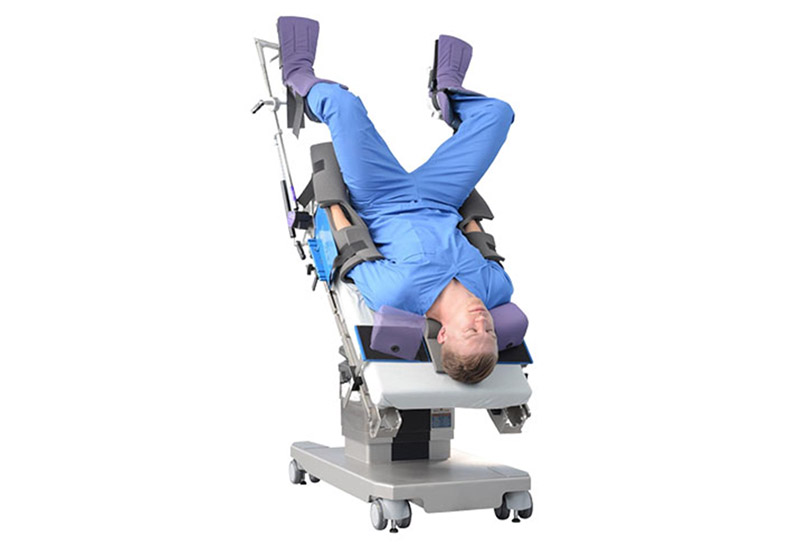
The Trendelenburg position is a form of postural treatment that involves placing a patient in a supine position on a bed, but it is inclined (10-35 degrees) such that the head is lower than the feet. It is regularly used during lower abdominal surgery to direct other organs towards the head, facilitating access to the site of interest. This position is also used in pelvic surgeries, central venous catheter (CVC) placement, and hypovolemic shock.
There are variations of this position to meet several surgical needs. They include the modified, reverse, and left Trendelenburg position.
What is the Reverse Trendelenburg Position?
The reverse Trendelenburg position is also known as anti- Trendelenburg. In this case, the patient is in a supine position with the head elevated instead.
It is used for head, neck, or upper abdomen surgeries.
What is the Modified Trendelenburg Position?
The modified Trendelenburg position is a partial supine position with the head level with the trunk while the legs are slightly elevated. This position is frequently used in hypotensive patients to aid venous return to the heart and restore adequate brain perfusion.
What is the Left Trendelenburg Position?
This position combines the lateral position, which involves lying on the left side, and the Trendelenburg position, usually at an angle of about 10°. It is used in respiratory interventions to prevent the escape of infected oropharyngeal secretions. As a result, this position reduces Ventilator-associated Pneumonia and colonization of microbes in the lungs.
Trendelenburg Position Vs. Reverse Trendelenburg Position
The Trendelenburg position is indicated for pelvic and lower abdominal surgeries, hypovolemic shock, and improvement of cerebral blood circulation. It also facilitates orotracheal intubation. On the other hand, indications for the reverse Trendelenburg position include:
● Head, neck, and shoulder surgeries
● Thyroid, gallbladder, and bile duct surgery
● Nasogastric tube insertion
● Hiatal hernia
● Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery
This position is more comfortable for patients as they can enjoy activities like television and reading.
What are the uses of the Trendelenburg position?
The Trendelenburg position is used to alleviate hypovolemic and neurogenic shock. Also, in gastrointestinal surgeries, this position is often used on the operating table, as it slightly shifts the organs toward the upper trunk for better access to the lower abdomen and pelvis. In addition, it is used in CVC placement and certain types of abdominal and genitourinary surgery. The Trendelenburg position also facilitates recovery in cases of vasovagal syncope.
Consideration for Trendelenburg Position
Before using the Trendelenburg position, healthcare workers usually consider risks and the potential for injury. Also, there are recommendations for repositioning.
Brachial Plexus Neuropathy
Patients may risk posture-related brachial plexus neuropathy due to prolonged operation time. The reason is that the shoulder braces cause extreme pressure on the acromion and clavicle. As a result, it damages the brachial plexus. Patients recover with physical therapy with analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Also, gabapentin is administered to relieve neuropathic pain.
Perioperative complications from extreme Trendelenburg positioning
Extreme Trendelenburg decreases blood pressure in the lower extremities, which in healthy individuals is compensated by the action of the baroreceptors. However, in the elderly and patients with atherosclerosis, it can cause severe ischemic disorders. Also, in patients with heart disease, this position significantly increases mean arterial and pulmonary capillary pressure, with greater demand for cardiac oxygenation. If the previous cardiac reserve is reduced considerably, it can trigger acute congestive heart disease or myocardial ischemia.
Furthermore, maintaining a steep Trendelenburg position for an extended period can increase jugular and intracranial venous pressure. Consequently, this decreases cerebral perfusion pressure.
Also, it causes restriction of pulmonary distension due to compression of the abdominal content on the pulmonary base, resulting in a more significant work of breathing.
Clinical recommendations for repositioning patients
High-angle Trendelenburg for an extended period can result in intraoperative injury. Therefore, there is a need for adequate monitoring to alleviate this risk. One way to prevent injury is to use the least possible angle to allow easy operation. Also, surgeons should administer crystalloids while initiating general anesthesia to limit the risk of cerebral edema.
In addition, for operations lasting over 4 hours, the nursing team should observe the patient every hour for a possible need to change position. The change would depend on the patient's physical and physiological condition. Another means to mitigate injuries is to relieve the patient of the Trendelenburg position for a brief period.
When do you put a patient in a Trendelenburg position?
Surgeons may employ the Trendelenburg position when there is a need to access the lower abdomen or pelvic organs. The position is utilized in colorectal and genitourinary surgeries. Due to the effect of gravity, the intra-abdominal organs leave these surgical sites to allow easy access. Another situation where a patient requires the Trendelenburg position is during CVC placement in the subclavian vein. Surgeons also employ this position for hypotensive shock.
Hospital Medical Equipment with Trendelenburg
Various pieces of hospital equipment on the market are designed to be adjustable to variants of the Trendelenburg position. They include hospital beds, operating tables, maternity beds, and stretchers. We'll discuss a few below.
Hospital Beds with Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg
● Fully Electric Automatic Hospital Beds with Remote Control for 5 Functions AG-BY003C Price: $1,190
The AG-BY003C automatic hospital bed is one of the most comfortable beds on the market, and it has a CPR function. The frame is rigid, made of electro-coated and powder-coated cold-rolled steel with a detachable ABS headboard and bed board. Also, it can accommodate a weight of about 250kg, thus suitable for bariatric patients.
The bed has five adjustments, including the Trendelenburg (12°), reverse Trendelenburg (12°), backrest (75° max), height (480-760mm), and footrest (40° max). Interestingly, these functions are controlled with the Linak motor for efficient movement. The hand-held remote control is used to initiate the desired adjustment.
The AG-BY003C automatic hospital bed is also equipped with four removable ABS handrails. Also, it has four wheels with center-controlled brakes.
● ICU Electric Hospital Bed with 10 Functions AG-BR006 Price: $3,705
The AG-BR006 ICU Electric Hospital Bed is your go-to bed for high-quality ICU services. Its frame is made of cold-rolled steel, while the bed board is of 10-part steel. On the other hand, the headboard, handrails, and footboard are ABS materials. Interestingly, the footboard has a nursing operator, and the bed can hold a weight of about 300kg.
In addition, the bed is equipped with CPR and seven remote-controlled adjustments. They include Trendelenburg (10°), reverse Trendelenburg (10°), backrest (75° max), height (640-860mm), footrest (45° max), and left and right lateral (0-12°). Also, the four noiseless wheels have a central locking system.
Operating tables with Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg
● Electro-Hydraulic Operating Table with SUS304 Stainless Steel Accessories AG-OT650 Price: $9,526
The AG-OT650 Electro-Hydraulic Operating Table is suitable for many surgeries, including plastic, gallbladder, cardiac, gynecology, etc. The frame and parts are made of easy-to-clean SUS304 stainless steel and can hold a maximum weight of 300kg.
It has both manual and motor-powered adjustments. While the former works for the headrest (60°/90°) and leg section (30°/90°), the latter works for Trendelenburg/reverse (30°), back plate flex (75°/50°), height (700-1040mm), reflex (230° 20° 30°), lateral tilt (20° left and right), and longitudinal sliding (300mm). The kidney level adjustment has an optional electric function. Rechargeable batteries power the electric parts of the bed. When fully charged, these batteries can last for 50 complete adjustments. Also, the bed has one key level reset.
● Electric Operating Table For Operating Theatre AG-OT030 Price: $6,536
The AG-OT030 electric operating table is suitable for all medical surgeries and x-rays. Its height (700-900mm), Trendelenburg (≥15°), reverse Trendelenburg (≥20°), lateral tilt (≥15°), and backward/forward (≥245mm) adjustments are motor driven. Other adjustable functions include the headrest (30°/45°), kidney raising (≥80mm), leg plate (≥90°), backplate (45°/5°), and front and rear left-turning plate. Also, the bed is equipped with luxurious wheels, can hold a maximum weight of 135kg, and has a rising speed of 3-16mm/s.
Hospital Stretcher with Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg
● Hospital Hydraulic Transport Stretcher with American Power Pump AG-HS001 Price: $1,984
The AG-HS001 hydraulic transport stretcher for emergency transfer is high-quality furniture with CPR and x-ray functions. Also, it can double as a hospital bed. It is equipped with hydraulic pumps used to facilitate adjustments. The frame is made of cold-rolled steel. Also, it comes with a waterproof mattress, polypropylene dust cover, handrails, and a detachable IV pole. The four wheels are equipped with brakes for patient safety. The dumper castors have a static and dynamic load capacity of 400kg and 250kg, respectively.
The possible adjustments with the hydraulic pumps include height (59~91cm), back section (≤75°), Trendelenburg/reverse (≤15°), and leg section (≤30°).
Maternity Bed with Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg
● Electric Maternity Bed with Remote Control AG-C500 Price: $4,630
The AG-C500 electric maternity bed is designed for the different stages of childbirth, including postpartum recovery. It has both mechanical and electrical operations. The electrical controls which are initiated by a foot pedal include the height (680-980mm), Trendelenburg (≥12°), reverse Trendelenburg (≥2°), and backrest (≥60°) adjustment. Interestingly, the bed is waterproof, and all adjustments are noiseless. The ABS frame has four wheels with brakes. Also, the maternity bed has a safe working load of ≥150kg.
The bed has a dirt basin beneath the table top and a detachable table that you can adjust as needed. Also, the handrail is made of high-strength plastic, and the leg section is detachable to be used when necessary. In addition, the footplate is equipped with an adjustable pneumatic spring for easy delivery.
In addition, it has an automatically charged lead-acid battery for emergencies. So, the battery jumps into action when there is a direct power outage.
Are there any potential risks associated with using the Trendelenburg Position, and what can be done to mitigate them
If not properly monitored, the Trendelenburg position can cause brachial plexus injury, respiratory distress, elevated intracranial venous pressure, and postoperative ischemic disorders. Also, when placed head down and legs elevated, patients may risk sliding off the table, resulting in severe head and spine injuries. In addition, patients with heart problems may be at risk of congestive heart disease.
The operating table must be padded with restraints to mitigate these risks to hold the patient in place. Also, the nursing staff must monitor the patient closely for any physiological or physical defects. In addition, the surgeons should take brief breaks from the Trendelenburg position, especially in extended operations.
Tips for Safer Trendelenburg Positioning
With the potential risks of Trendelenburg Positioning, here are tips for a safer procedure:
● Use the procedure's least possible time and tilt angle when using the Trendelenburg position. Greater tilt degree increases the risk of complications.
● Gradually relieve the patient of the position for the body to adjust to blood volume changes.
● Protective foam or gel paddings prevent skin shearing and nerve injuries, especially between joints. Protect the arm with sleds. Also, the shoulder braces should be adequately padded to avoid soreness and sliding from the OT table.
● Before positioning, consider the patient's BMI, respiratory status, possible eye defects, and other conditions.
● Beanbag restrains are safer than straps.
● Finally, check the face regularly for edema, especially in lengthy procedures over three hours. If you notice any facial swelling, relieve the patients of the Trendelenburg position.
When should the Trendelenburg position not be used?
Surgical access is not the only goal of the Trendelenburg position. The position also considers patient comfort and safety. Therefore, weighing its risks against benefits, this position should not be used for patients with head injuries, pulmonary disorders, decreased right ventricular ejection fraction, glaucoma, and other eye defects.
FAQ
Is the Trendelenburg position safe?
The Trendelenburg position facilitates surgical access in pelvic and lower abdominal surgeries. However, if not correctly monitored, some complications like edema, respiratory distress, and never injuries. Hence, patients in this position require adequate attention.
What are the benefits of Trendelenburg?
The Trendelenburg position directs the abdominal organs towards the trunk for easy access to abdominal and pelvic viscera. Thus, it is helpful in colorectal and genitourinary surgeries. It is also vital in the early treatment of hypotension.
Is fowler's position the same as Trendelenburg position?
No! Unlike the Trendelenburg, the fowler's position is a semi-sitting position in which the bed's backrest is elevated between 45° to 60°.
Does Trendelenburg decrease heart rate?
The Trendelenburg position raises venous return and triggers baroreceptors to increase vagal nerve activity and subsequently decrease heart rate.
What does a positive Trendelenburg sign mean?
The Trendelenburg sign indicates a hip defect identified during a physical exam. It has no relationship with the Trendelenburg position. A positive Trendelenburg sign means the hip abductor muscles are weak.
Summary
The Trendelenburg position is employed in lower abdominal surgeries to improve access to the site of interest. Currently, various manufacturers of hospital beds, OT tables, and stretchers incorporate this position into their designs to ease the work of surgical staff. Before employing this position, the surgical team must ensure the benefits outweigh the risks. Also, they should follow the necessary guidelines for patient safety and ease of the procedure.
No posts found
Write a reviewRecent posts
- How Much Does a Video Laryngoscope System Cost?
- CPR Machine: How Much Does It Cost?
- Types Of Beds In Hospitals: Buy the Best Hospital Beds Online
- How Much Does an ICU Bed Cost?
- Find The Different Types of Medical Lighting Systems Online
- Complete Guide To Oxygen Therapy:Best Oxygen Machine
- What Is Durable Medical Equipment?
- Medical Stainless Steel Table: How to Choose the Suitable One for Hospitals
- Why Should You Upgrade Your Medical Equipment?
- How To Choose The Correct Armboard?
- Need Help?Talk to our Experts!
- Give Us A Call
- info@medwish.com
- Financial Service