Not satisfied with the unit price? Get a free quote on bulk quantities within 8 hours.
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
A Comprehensive Guide to Buying a CT Scanner
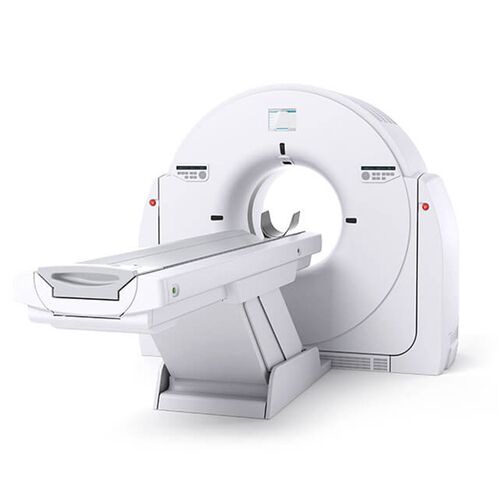
Health care practitioners need the help they can get in diagnosing medical conditions. From stethoscopes to mammography machines down to CT Scanners, these devices provide an insight into what’s going on in a patient’s body.
This guide discusses what a CT scanner is and examines vital considerations to make before buying one.
What is a CT Scanner?
A CT scanner is a massive machine in the shape of a donut with a narrow tunnel running through the middle.
This device takes an array of X-ray images at different angles around the body. It combines them using computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside the body. CT scanners are commonly used in medical diagnostics.
Images obtained from CT scans can provide more detailed information than regular X-rays can on their own.
What is the CT Scanners Used For?
Alongside X-rays and medical ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scanners have quickly emerged as one of the most useful diagnostic tools in medical imaging since their introduction.
It has more recently been used for preventive medicine or screening for diseases, such as CT colonography for individuals with a substantial risk of colon cancer or full-motion heart scans for individuals with a high risk of cardiovascular disease.
The benefits of CT Scanners
The CT scanner is preferable for the following reasons:
- It is painless, does not involve invasion, and provides accurate results.
- It is capable of capturing images of the bone, soft tissue, and blood arteries all at the same time.
- In contrast to more traditional x-rays, CT scanners produce incredibly detailed images of various tissue types.
- It provides a quick and easy procedure.
- It can detect internal injuries and bleedings early enough in an emergency, which can assist save lives.
- When compared to MRI, CT is less sensitive to patient movement.
What Is The Difference Between CT Scans And MRI?
Both computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to obtain images from within the body, but they do so in quite different ways.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves and magnets, whereas computed tomography (CT) scans use X-rays. This is the primary distinction between the two.
The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment can be rather noisy, so it is common practice to provide patients with earplugs or headphones to help them better tolerate the noise.
Fat and water molecules in your body reflect a continual magnetic field and radio frequencies as they bounce off of one other.
After that, radio waves are sent to a receiver built within the apparatus. This receiver then converts the radio waves into an image of the body that radiologists may use to diagnose problems.
On the other hand, a CT scan captures many X-ray images of the patient's body from various angles, and it is also a reasonably quiet procedure.
Because of the magnetism of MRI machines, patients with specific metal implants cannot be examined with these machines, although MRI machines produce more detailed images than CT machines.
Components of the CT scanner
CT scanners are equipped with a scanning gantry, slip rings, an x-ray generator, a computer system, a console panel, and a physician's viewing console.
Furthermore, most CT Scanning systems incorporate a laser printer for transmitting CT scans on film. However, workstation viewing and electronic archiving are more commonly employed.
The gantry is the donut-shaped CT Scanner portion that houses several components required to generate and detect x-rays. The gantry can rotate thanks to slip-rings continuously.
This avoids the need to straighten twisted system cables. Helical scan modes are made possible by allowing the gantry frame to spin continually.
Factors to consider before purchasing the right CT Scanner
When buying a CT Scanner, it is important to note the following:
Slices Count
The term "slice" refers to the number of detector rows in a CT's z-axis. In a 4-slice CT, for example, four slices of data are collected per rotation of the gantry. The initial CT scanners produced single-slice CT (SSCT) pictures, but now multi-slice CT scanners are available.
The slice count has the most significant impact on the time it takes to perform a CT scan. The benefits of a CT scanner with a more considerable number of slices are as follows:
- Scan times are reduced, leading to lower radiation exposures.
- Images with more detail and fewer artifacts
- Increased patient throughput
- Advanced imaging options, such as cardiac examinations
There are a variety of slice counts useful for different situations, and let’s examine them below
4- and 8-slice CT Scanners: If you manage a veterinary clinic or a department with a small number of patients and there is no need for a quick diagnosis, then a CT scanner with four or eight slices is a decent option for you to consider.
These scanners are among the most affordable on the market, but their scan times are the longest. In addition to this, their power is significantly lower. They are appropriate for follow-up procedures where time is not a consideration.
16-slice CT Scanners: The 4- or 8-slice scanners are slower than the 16-slice scanners, so many medical clinics, and radiology departments that experience a somewhat consistent flow of patients opt for the 16-slice scanner instead.
These devices are excellent for standard examinations. Because of this, the 16-slice scanner is appropriate for use in emergency rooms and urgent care centers, in addition to busy imaging facilities, as a 16-slice scanner is a durable workhorse. Examples include the Philips MX 16 Slice, and the GE Brightspeed Elite 16 Slice
32-40 slice CT Scanners: CT scanners with 32-40 slices can commonly be found in the same kinds of facilities as the 16 slice model.
When compared to the 16-slice, the distinction is that the additional slices provide more coverage for each gantry rotation, which in turn reduces the amount of time it takes to do the scan. As a result, the image is not as significantly impacted by motion artifacts as lower slice models. The Toshiba Aquilion 32-Slice is an example.
64- slice CT Scanners: The 64-slice CT has become the industry standard for imaging centers and hospitals. Because of the decreased amount of time needed for the scans, more complex tests, such as cardiac examinations, can now be carried out. Its speed and accuracy make it well-suited for use in medical clinics with a moderate to the high number of patients.
In cardiology, doctors can use a 64-slice CT scanner to do cardiac tests; however, the patient's pulse rate must first be slowed down. On the other hand, for more advanced cardiac procedures, more slices are preferable. Both the GE LightSpeed 64-Slice and the Phillips Brilliance 64 are two examples.
128- slice CT Scanners: These high-quality CT scanners, which can produce whole-body scans in a matter of seconds and provide an astonishingly clear 3D image of any organ, range from 128 to 320 slices and are among the best in the industry.
Within a typical clinical environment, the capabilities of these scanners are frequently excessive and unnecessary. As a result, you will typically find them supporting specialist practices, like cardiac departments, research centers, or areas with very high patient traffic.
The Philips Ingenuity 128-Slice and the Toshiba Aquilion CX 128-Slice are two examples of such machines.
Application
When purchasing a CT scanner, you would do well to consider the purpose you would use it for.
For most general imaging purposes, a 16-slice scanner should be adequate. This slice count also works well for ERs, urgent care centers, and hospitals or high-volume imaging centers.
However, if you use the scanner for cardiac imaging, you should go for 64-slice scanners with higher speeds. This is because such scanners move fast enough to capture images that freeze cardiac motion and prevent motion blur. You should also ensure that it has a Motion-Correction algorithm and Cardiac Metal Artifact Reduction Software to reduce retakes and produce more precise images.
Suppose your practice requires vascular procedures like angiography. In that case, you should note that CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) is an alternative for diagnosing stenosis or aneurysms in vessels. It is technically simpler than X-ray angiography and carries a lower risk of complications.
However, even with modern CT scanners, the detail resolution is lesser (the median voxel size is between 0.5 and 1 millimeter). Hence, the higher the detail resolution of the scanner you purchase, the better it’ll be for your practice.
CT scans are also commonly used in evaluations of trauma patient injuries. Suppose you would be using them for this purpose. In that case, you should avoid earlier models, which are limited by the length of their scanning time and location, as this can be particularly challenging for unstable trauma patients. Instead, go for newer 64-slice models with increased area coverage, allowing you to perform scans faster.
The X-Ray Tube
As it generates X-rays, the X-ray tube is one of the most vital components of a CT scanner, and it is costly to replace.
X-ray tubes are characterized by the heat they can withstand, expressed in MHU (Mega Heat Unit). The greater the MHU rating, the more heat the tube can withstand and the more examinations it can conduct.
Due to the relative expense of a new tube, there is considerable interest in predicting the CT tube's expected lifespan. However, various manufacturers measure it in different ways.
Milliampere Seconds (mAs): This offers information on the duration of exposures and the amount of power that has passed through the tube. This is the best method for determining the tube's remaining lifespan.
Scan Seconds: This measures the duration of the tube's exposures or how long the tube has been used. However, this does not represent the amount of power or heat passed through the tube.
Clicks/Count: This method of determining CT tube count indicates the number of exposures performed by the tube. However, it does not provide the power usage expended during these exposures.
Total Patient Exams: This is the sum of all individual X-ray examinations that have been conducted with the tube. It does not include information on the length of the examinations or the amount of effort they took.
Warranty and Installation
When buying CT Scanners, it is best to go for those with a warranty as these are likely to be more reliable. Ensure that you make the most out of your money by going for equipment that will provide you assurance in terms of durability and the services provided.
Some manufacturers also offer installation support for a fee or may recommend third-party installation services providers. Whichever option is available to you, ensure that the installation is done well and follows the manufacturer's specifications.
Budget
The significant factors that affect the price of a CT scanner are brand, condition, slice count, data processing features, model, and particular usage. Weigh the cost of the machine against the services you need, ensuring you don’t end up paying too much for a unit you don’t need. For example, it may not be cost-effective to buy a 128-slice scanner for a small scanner. Hence, weigh your needs against the costs.
CT Scanner Price Guide
The prices of CT scanners vary and are majorly dependent on the brand and features present in the machine.
Some of the models of different brands as well as their prices are as follows:
- GE BrightSpeed Elite: $106,890
- Canon-Toshiba Aquilion One: $ 696,550
- Siemens Somatom Definition 64: $ 165,640
- Philips Ingenuity:$ 359,393
- SZBY-CT16 CT Scan Machine:$277,200
- 3D Panorama Dental CT MDE-3D: $59,643
Where to Buy CT Scanners in Bulk With Wholesale Pricing
Hospitals and other health bodies can purchase CT Scanners at Medwish. We are a global B2B platform that specializes in supplying high-grade medical facilities for hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare institutions.
With our vast network spread across several countries, you can get in touch with us from around the world to order CT Scanners or other medical equipment.
Medwish also offers product financing and hospital project financing options to help secure financial collaborations and help you get the best CT Scanners quickly.
Medwish Wholesale Price Advantage
Purchase CT Scanners from Medwish to get more medical supplies for your hospital or health center while saving money without sacrificing quality or safety.
Medwish offers quality CT Scanners at competitive prices and provides financing options for healthcare institutions who wish to purchase these devices in bulk. So before making your final decision, be sure to check out what we have on offer.
No posts found
Write a reviewRecent posts
- How Much Does a Video Laryngoscope System Cost?
- CPR Machine: How Much Does It Cost?
- Types Of Beds In Hospitals: Buy the Best Hospital Beds Online
- How Much Does an ICU Bed Cost?
- Find The Different Types of Medical Lighting Systems Online
- Complete Guide To Oxygen Therapy:Best Oxygen Machine
- What Is Durable Medical Equipment?
- Medical Stainless Steel Table: How to Choose the Suitable One for Hospitals
- Why Should You Upgrade Your Medical Equipment?
- How To Choose The Correct Armboard?
- Need Help?Talk to our Experts!
- Give Us A Call
- info@medwish.com
- Financial Service





