Not satisfied with the unit price? Get a free quote on bulk quantities within 8 hours.
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
- Ward Nursing
- Emergency & First Aid Care
- OR Room & Apparatus
- Maternal & Child Care
- Medical Imaging
- Clinical Trial & LAB
- Vital Signs Monitoring System
- Rehabilitation Therapy
- Sterilization& Disinfection
- ENT& Aesthetic Equipment
- Medical Consumables
- Hospital Solution
- Hemodialysis
- Veterinary Equipment
- FDA Product
- CE Product
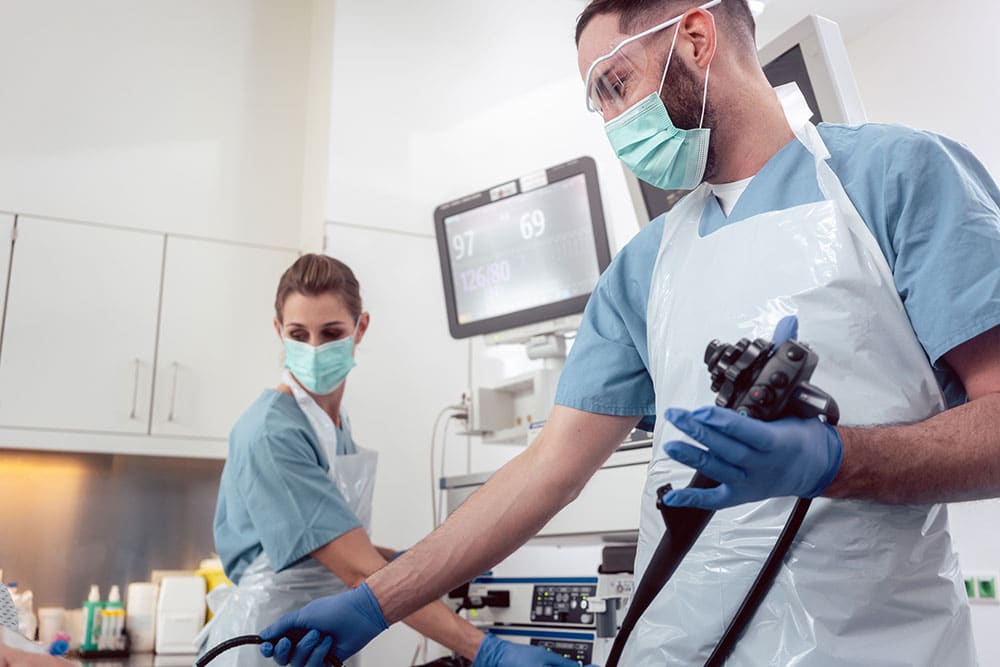
Endoscope Equipment System: Types, Functions ,Prices Guide
Full Catalog and Price List of Endoscope
When it comes to endoscopes and other associated instruments, according to We Buy Endoscopes, an industry leader in endoscopic equipment repair, endoscopes, and other related tools, can cost tens of thousands of dollars. Even for medical professionals who own and operate offices, this is not a modest charge. It's a huge problem that We Buy Endoscopes is working to solve with a careful mix of selling, purchasing, and repairing services that help save expenses.
What is an Endoscope?
A long, thin, flexible tube with a light and camera at one end is known as an endoscope. On a television screen, images of the interior of your body are displayed. Endoscopes can be inserted into the body by the mouth and down the throat or via the bottom.
An endoscope can be inserted into the body through a small cut (incision) in the skin when doing keyhole surgery.
Depending on the location and the use of the endoscope, the tool is redesigned for that specific purpose and can be specifically named to fit the specific job it’s doing. Examples are Cystoscope, Esophagoscope, Gastroscope, Laparoscope Etc.
What is Endoscopy?
Endoscopy is a non-surgical treatment that examines the digestive tract of a person. Your doctor can examine photos of your digestive tract on a color TV monitor using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera connected to it.
An endoscope is inserted easily through the mouth and neck and into the esophagus during an upper endoscopy, allowing the doctor to examine the esophagus, stomach, and upper section of the small intestine.
Endoscopes can also be inserted through the rectum into the large intestine (colon) to check this section of the intestine. Depending on how far up the colon is inspected, this technique is referred to as sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy.
Borescope VS Endoscope
Both borescopes and endoscopes are inspection cameras. If you're looking for a new borescope or endoscope, you could have come across the other word while searching. While the two instruments have similar names and looks, their uses are vastly different. Before making a purchase, it's critical to understand the differences between these two essential gadgets. The incorrect instrument may not be suitable for your company's needs.
A borescope is a specialized instrument that allows you to see within small, hard-to-reach places. Borescopes make previously inaccessible, tiny, and dimly lit areas visible. Modern borescopes have high-definition cameras that allow users to see these difficult-to-reach places in great detail. Borescopes have lights built in to illuminate dark regions.
While an endoscope is a type of borescope, it’s helpful to note that while all endoscopes are borescopes, not all borescopes are endoscopes!
When compared to traditional borescopes, endoscopes are more accurate and polished. While both devices accomplish comparable duties, endoscopes are generally employed in regions with a greater danger of mistake. Endoscopes are made up of a small camera connected to a long, flexible cable. Users may move the camera around in extremely small places by twisting the cord. Endoscopes, like borescopes, include an integrated LED light that illuminates the region without blinding the camera.
Components Of an Endoscope
Endoscopes include several basic components. However, the specifics vary depending on the activities they are meant to do.
- An endoscope consists of the following components:
- A tube that could be either flexible or rigid
- An image of the patient's internal system is transmitted to the operator or viewer through a lens (this is generally a relay lens in rigid endoscopes or multiple fiber-optics for fiberscopes)
- A light-transmitting technology that improves the visibility of the region being inspected
- An additional channel to allow medical instrument manipulators during surgical
- An eyepiece (Images from within the patient are transmitted to a screen for viewing and capturing in videoscopes without eyepieces.)
- A light guide plug that links to the illumination source: This will be heavier in videoscopes than for other types of scopes.
- An umbilical connection (or universal cord) connects the light guide plug to the scope’s control head.
- The control head, which houses the angulation-control knobs and any suction or water functions, allows the operator to govern the scope's performance.
- The insertion tube is inserted into the patient's body and, predictably, gets heavily polluted throughout the operation - the distal end has videoscopes and microchips and holes for air or water functions and suction.
- A smaller circumference
- Rigid Endoscopes: Endoscopes that are put into the body through natural holes and laparoscopes that are implanted by incisions are the two types of rigid endoscopes. Rigid endoscopes are short metal tubes with a light source and a magnifying device. This type of endoscope is used in urology, gynecology, otolaryngology, and general surgery. The most popular type of endoscope on the market is the rigid endoscope. They're used in most surgical endoscopic procedures to let endoscopists see the surfaces of the organs.
- Flexible Endoscopes: Flexible endoscopes can reach the furthest reaches of the human
- Dimensional and ergonomic aspects of the instrument have a direct impact on the equipment's usage.
- Depending on the use case, one might want to opt for an endoscope that is water-proof or at least water-resistant. These types are usually wireless, and wifi enabled.
- The resolution of the device and its compatibility with modern endoscopic systems impact the picture quality and, consequently, the efficiency of the equipment.
- The features responsible for the direction and field of vision are the angular field, focus range, and bending angle of the distal end; instrument channel compatibility with accessories and its diameter.
- Another important feature is the amount of storage in the device and the support of removable storage media.
- Cleaning compliance and/or the potential of disinfectant immersion.
- Karl Storz endoscope between $2000-$4000
- despatch endoscope $20-$40
- endoscope Olympus: this costs between $2000-$3000
(the source of this light is usually based outside of the body, directed through optical fibers)
operations.
External components of flexible endoscopes include:
The distal end is close to the bending portion.
Application of an Endoscope
Borescopes are commonly used to investigate mechanical things, whereas endoscopes are utilized to examine living organisms. Endoscopes have the following advantages over borescopes:
- A higher capacity to move
- A greater level of specificity
Endoscopies are procedures in which a doctor examines a patient's digestive tract by inserting an endoscope through their mouth. Colonoscopies are also performed using endoscopes. An endoscope's field of vision is significantly smaller than a borescope at 90 degrees. Endoscopes are substantially more expensive than other types of medical equipment since they are medical-grade.
Types of Endoscopes
Endoscopes are divided into two groups based on their design features:
body, providing invaluable diagnostic information, particularly in gastroenterology, pulmonology, and gynecology. Fiber endoscopes and video endoscopes are the two major types of flexible endoscopes. Fiber endoscopes are less complicated to make and are mostly used for observation. Video endoscopes, which come with a video camera, a large instrument channel, and water and air supply systems, are suitable for surgical operations in the cavity being inspected.
To select the best decision, you must first determine what the gadget will be used for. It is important to define the sorts of manipulations that will be performed – diagnostic or therapeutic – and the bodily areas that will be evaluated.
What to look out for when buying an endoscope
- Dimensional and ergonomic aspects of the instrument have a direct impact on the equipment's usage.
- Depending on the use case, one might want to opt for an endoscope that is water-proof or at least water-resistant. These types are usually wireless, and wifi enabled.
- The resolution of the device and its compatibility with modern endoscopic systems impact the picture quality and, consequently, the efficiency of the equipment.
- The features responsible for the direction and field of vision are the angular field, focus range, and bending angle of the distal end; instrument channel compatibility with accessories and its diameter.
- Another important feature is the amount of storage in the device and the support of removable storage media.
- Cleaning compliance and/or the potential of disinfectant immersion.
- The level of control permitted by the equipment is another thing to look out for.
- The LED light cost: The current standard light source is a Xenon-based arc lamp, which
generates a wide spectrum over the visible range remarkably similar to daylight. Xenon lamps are powerful yet wasteful, requiring over 300W of electrical power to provide just around 1W of optical output. One of the most important requirements in endoscopy is lighting. If the lux level on the examined region is less than the threshold, the picture obtained may be distorted, resulting in an incorrect result.
It's also worth studying the pricing policies of endoscopic equipment makers. Because financial resources for publicly financed health care are typically limited, emphasis should be given to reliable equipment from established manufacturers who can provide appropriate extended service maintenance for their goods. If their executive team is confident in their business return, private clinics may afford to use pricey cutting-edge equipment accessible on the market.
Endoscopes are generally expensive to buy, but Medwish.com offers great deals wholesale. MedWish.com offers a wholesale price advantage when endoscopes are bought in bulk.
Endoscope Price Guide
Endoscope brands and their prices
- Karl Storz endoscope between $2000-$4000
- despatch endoscope $20-$40
- endoscope Olympus: this costs between $2000-$3000
No posts found
Write a reviewRecent posts
- How Much Does a Video Laryngoscope System Cost?
- CPR Machine: How Much Does It Cost?
- Types Of Beds In Hospitals: Buy the Best Hospital Beds Online
- How Much Does an ICU Bed Cost?
- Find The Different Types of Medical Lighting Systems Online
- Complete Guide To Oxygen Therapy:Best Oxygen Machine
- What Is Durable Medical Equipment?
- Medical Stainless Steel Table: How to Choose the Suitable One for Hospitals
- Why Should You Upgrade Your Medical Equipment?
- How To Choose The Correct Armboard?
- Need Help?Talk to our Experts!
- Give Us A Call
- info@medwish.com
- Financial Service






